Introduction to Building Thermography: Detecting Non-Visible Defects
Building thermography is a powerful tool used to identify non-visible defects in structures. By utilising infrared technology, thermographers can detect anomalies that are not visible to the naked eye.
Building thermography involves the use of infrared cameras to capture thermal images of buildings and structures. These cameras detect the infrared radiation emitted by object surfaces and convert it into a visual representation of temperature values. By analysing these images, the temperature variations and heat gradients, thermographers can identify areas of concern that may indicate the presence of defects or anomalies.
Thermography is based on the principle that all objects emit infrared radiation, which is directly related to their temperature. By measuring and visualising this radiation, thermographers can identify temperature differences that may indicate hidden issues within a building.
Building thermography relies on the use of infrared cameras, also known as thermal imaging cameras. These cameras are equipped with sensors that can detect and measure the infrared radiation emitted by objects. The captured data is then processed and converted into a thermal image, where different colors represent different temperatures.
During a thermographic inspection, a thermographer scans the building or structure using the infrared camera. The camera captures the thermal patterns and displays them in real-time on a screen. The qualified thermographer analyses these patterns to identify temperature variations that may indicate the presence of defects not seen by the eye.



The Basics of Building Thermography
Building thermography is a non-destructive testing technique that uses infrared technology to detect and measure heat patterns in buildings. By capturing thermal images of the building’s surfaces, thermography can identify areas of potential energy loss, moisture intrusion, and insulation deficiencies.
This allows building professionals to pinpoint areas that require attention and prioritise energy-saving measures.
Applications of Building Thermography
Building thermography has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the key applications include:
- Energy Efficiency Assessments: Thermography can be used to identify areas of heat loss or air leakage in buildings, helping to improve energy efficiency and reduce utility costs.
- Electrical Inspections: Thermography can detect overheating electrical components, such as faulty wiring or overloaded circuits, preventing potential fire hazards.
- Moisture Intrusion Detection: Thermography can identify areas of moisture intrusion, such as leaks or water damage, which can lead to mold growth and structural issues.
- Roof Inspections: Thermography can detect areas of heat loss or moisture accumulation in roofs, helping to identify potential leaks or insulation problems.
- Building Diagnostics: Thermography can be used to assess the overall condition of a building, identifying structural defects, insulation issues, and other hidden problems.
The Role of Qualified Thermographers
Thermographers play a crucial role in conducting building thermography inspections. These professionals are trained in the use of infrared cameras and have the expertise to interpret thermal images accurately. Their role involves:
- Conducting Calibrated Inspections: Thermographers perform thorough inspections of buildings and structures using infrared cameras, ensuring that all areas of concern are captured.
- Interpreting and Analysing Thermal Images: Thermographers analyse the captured thermal images, identifying temperature variations and potential defects.
- Reporting and Recommendations: Thermographers provide detailed reports to clients, highlighting the identified issues and recommending appropriate actions for remediation.
- Continued Education: Thermographers stay updated with the latest advancements in thermography technology and techniques to ensure accurate and reliable inspections.
Building Thermography Services
Whether it’s a residential, commercial, or industrial property, investing in building thermography services is a smart decision that can lead to long-term savings and a more sustainable future.
Contact us today to schedule a thermographic inspection and unlock the potential for a more energy-efficient and cost-effective building.
The Benefits of Building Thermography
Building thermography offers numerous benefits for both property owners and professionals involved in the construction and maintenance of buildings. Some of the key benefits include:
- Non-Destructive Inspections: Non-destructive inspections refer to a range of techniques and methods used to assess the integrity and quality of materials, components, or structures without causing any damage or alteration to them
- Early Detection of Defects: Thermography will identify defects early on, prompt repairs can be made, preventing further deterioration and minimizing potential risks. This proactive approach helps to maintain the integrity of objects or systems, ultimately saving time, costs, and resources in the long run.
- Cost Savings: By identifying issues before they escalate, thermography can help save on costly repairs and minimise downtime.
- Improved Safety: Thermography can detect potential fire hazards, electrical faults, and other safety risks, ensuring the safety of occupants and workers.
- Energy Efficiency: Thermography plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency and minimising utility costs by detecting areas of heat loss or air leakage. Through the use of infrared technology, thermographic cameras can identify thermal patterns and anomalies that signify energy wastage in buildings. By pinpointing these areas, building owners and managers can take appropriate measures to improve insulation, seal gaps, and optimise the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. This proactive approach not only conserves energy but also significantly reduces utility expenses, making thermography an invaluable tool in promoting energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Enhanced Building Performance: Thermography can help optimise the performance of buildings by identifying and addressing issues that may impact comfort, durability, and functionality.
Several case studies and statistics highlight the effectiveness of building thermography in detecting non-visible defects. For example, a study conducted by a leading thermography company found that 80% of electrical faults were detected through thermographic inspections, preventing potential fire hazards and equipment failures. In another case study, a thermographic inspection of a commercial building revealed hidden moisture intrusion in the walls, which, if left undetected, could have led to extensive mold growth and structural damage.
Building thermography services provide valuable information about the energy efficiency and structural integrity of a building. With the use of infrared cameras, trained professionals can detect heat loss, air leakage, and insulation issues that may not be visible to the naked eye. By conducting a thermographic inspection, building owners and managers can identify areas of concern and take appropriate action to improve energy efficiency, reduce utility costs, and enhance occupant comfort.
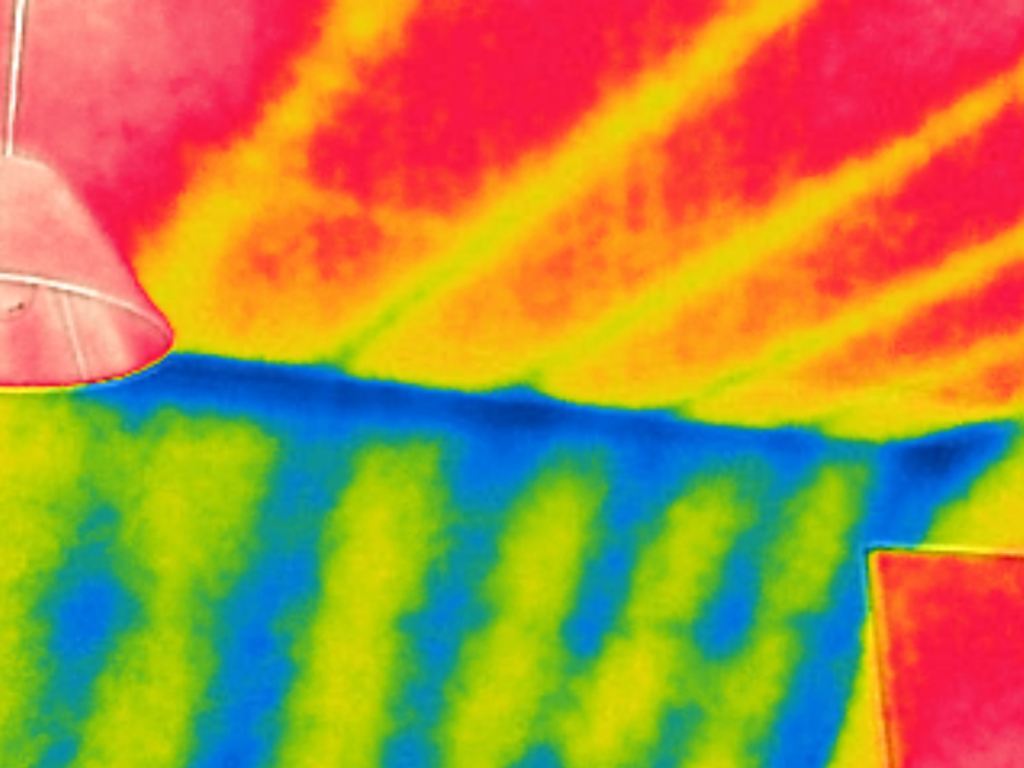
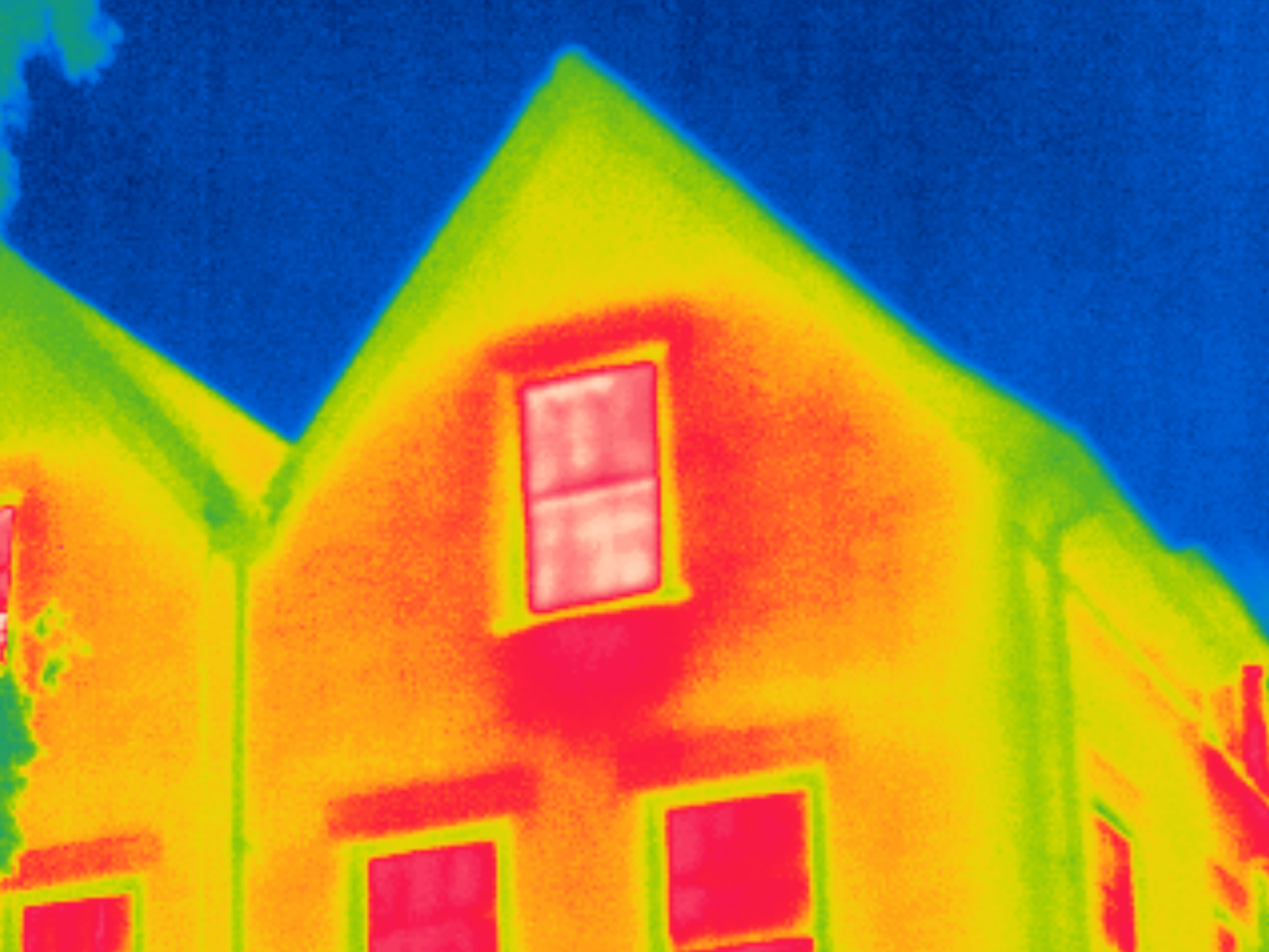
Missing Skeiling Insulation
Missing Wall Insulation
Air Leak Penetrating Wall Cavity
Building thermography is a valuable tool for detecting non-visible defects in structures. By utilizing infrared technology, thermographers can identify temperature variations that may indicate hidden issues. The applications of building thermography are vast, ranging from energy efficiency assessments to electrical inspections and moisture intrusion detection.
Thermographers play a crucial role in conducting thermographic inspections, ensuring accurate interpretation of thermal images and providing detailed reports to clients. The benefits of building thermography include early defect detection, cost savings, improved safety, energy efficiency, and enhanced building performance.
With its proven effectiveness and numerous benefits, building thermography is an essential component of building maintenance and safety. By investing in regular thermographic inspections, property owners can identify and address non-visible defects, ensuring the longevity and safety of their buildings.
Thermal roof inspection by drone is a cutting-edge technology that uses unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with thermal imaging cameras to conduct thorough and efficient inspections of roofs, enabling professionals to identify potential issues such as leaks, heat loss, and insulation problems.
By capturing and analysing the thermal patterns emitted by electrical components and circuits, this inspection method can detect problems such as overheating, loose connections, overloaded circuits, and faulty equipment. This proactive approach helps ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical installations by identifying potential hazards before they cause accidents or disruptions.
Thermal Imaging
Quantitative and qualitative thermography are two essential methods in thermal imaging analysis. Quantitative thermography measures exact temperature values, while qualitative thermography focuses on pattern recognition. Both play a crucial role in building inspections, electrical fault detection, and industrial diagnostics. Understanding their differences helps professionals choose the right approach for accurate thermal assessments. Drone Media Imaging provides expert thermographic services, ensuring precise, reliable results. Contact us today for professional thermal imaging analysis.
The Importance of Building Thermography Surveys in the UK and the Role of Level 3 Certified Thermographers Building thermography is a non-destructive diagnostic method that uses infrared technology to detect thermal anomalies in structures. In the UK, this approach has become critical for energy efficiency, structural integrity, and safety assessments, especially with rising environmental standards and compliance requirements like BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method. Applications of Building Thermography Energy Efficiency Audits: Identifying heat [...]





