Thermal Bridging in Commercial Buildings
Unveiling the Hidden Costs: Thermal Bridging in Commercial Buildings

In the intricate world of commercial building design and construction, one often-overlooked factor plays a crucial role in energy efficiency – thermal bridging. This phenomenon, where heat easily transfers through the fabric of a building, not only impacts the comfort of its occupants but also significantly increases operational costs. The effects of thermal bridging on heat loss and its financial implications for commercial buildings, can be assessed by the itilisation of sophisticated technique of thermal imaging used to identify and mitigate this issue.
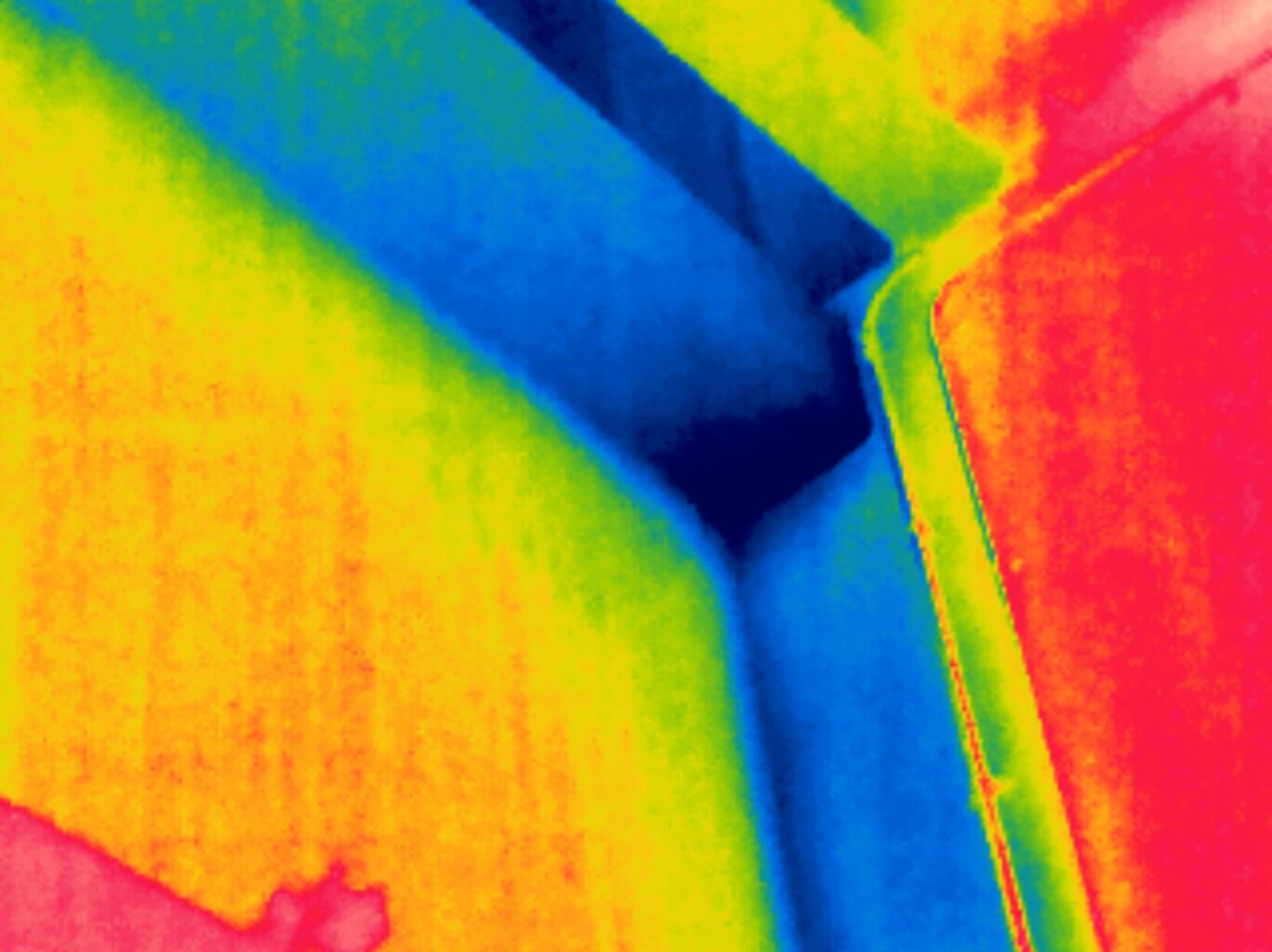
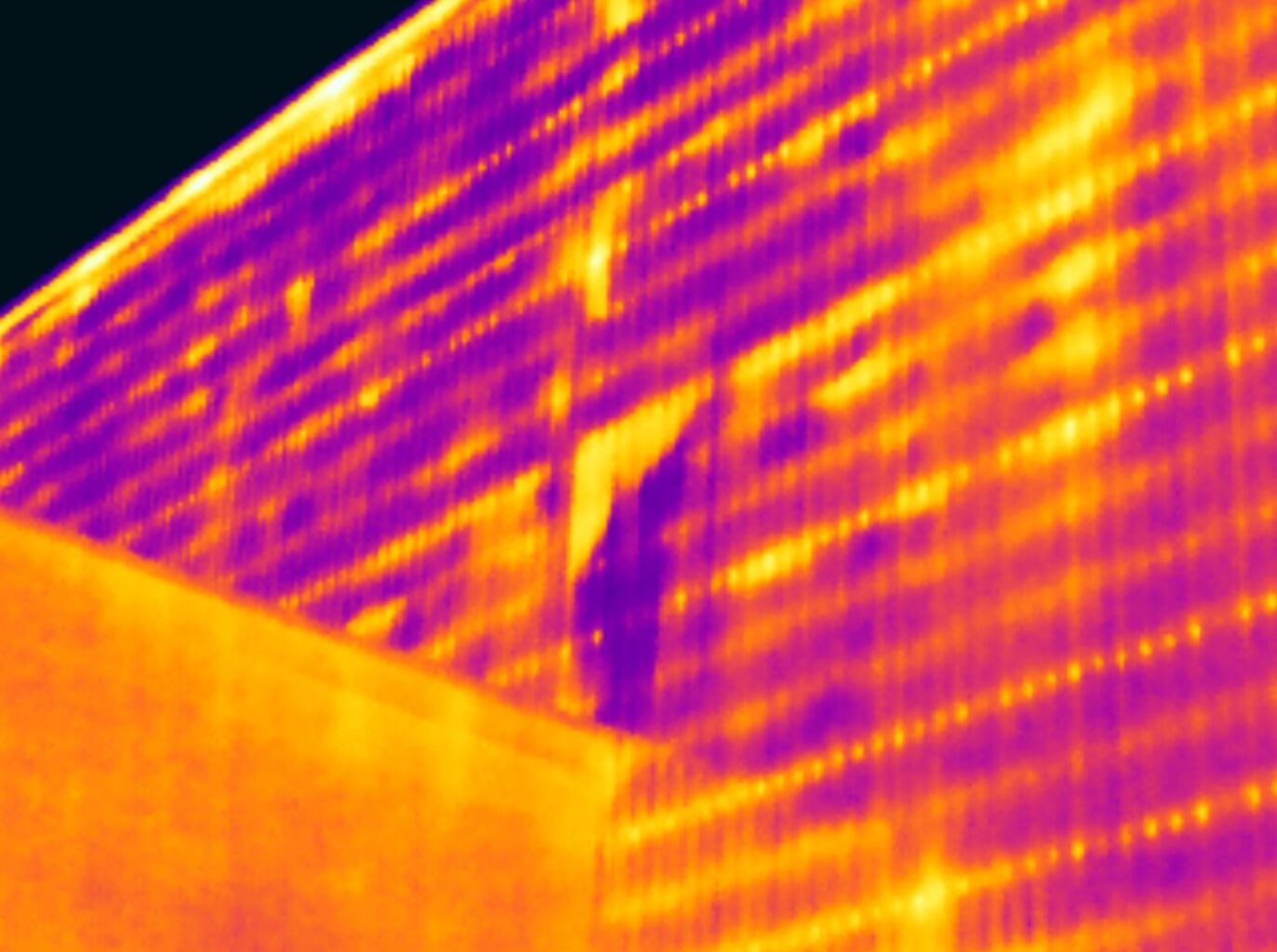
Thermal bridging through steel building supports
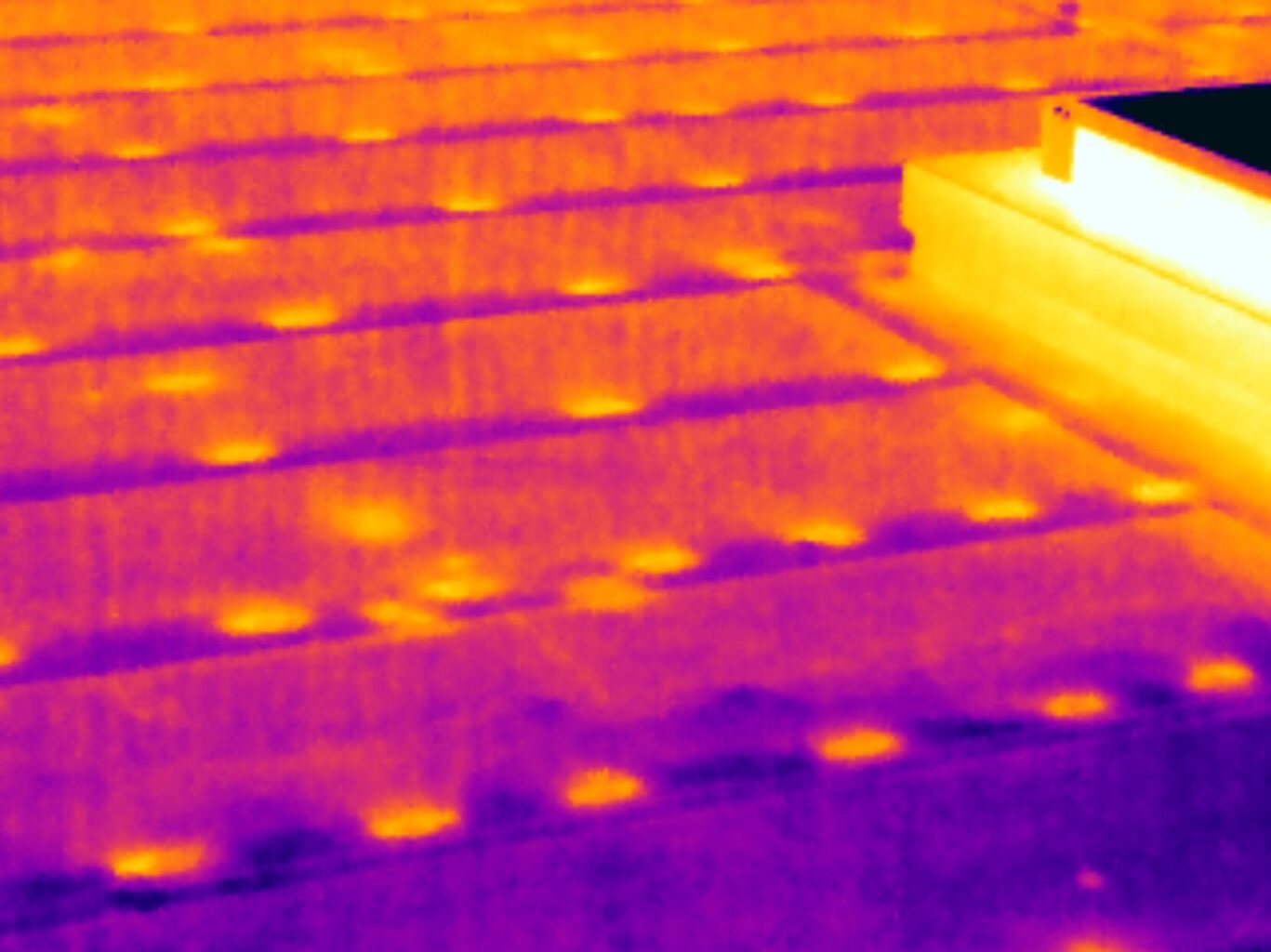
Thermal bridging through roof fixings
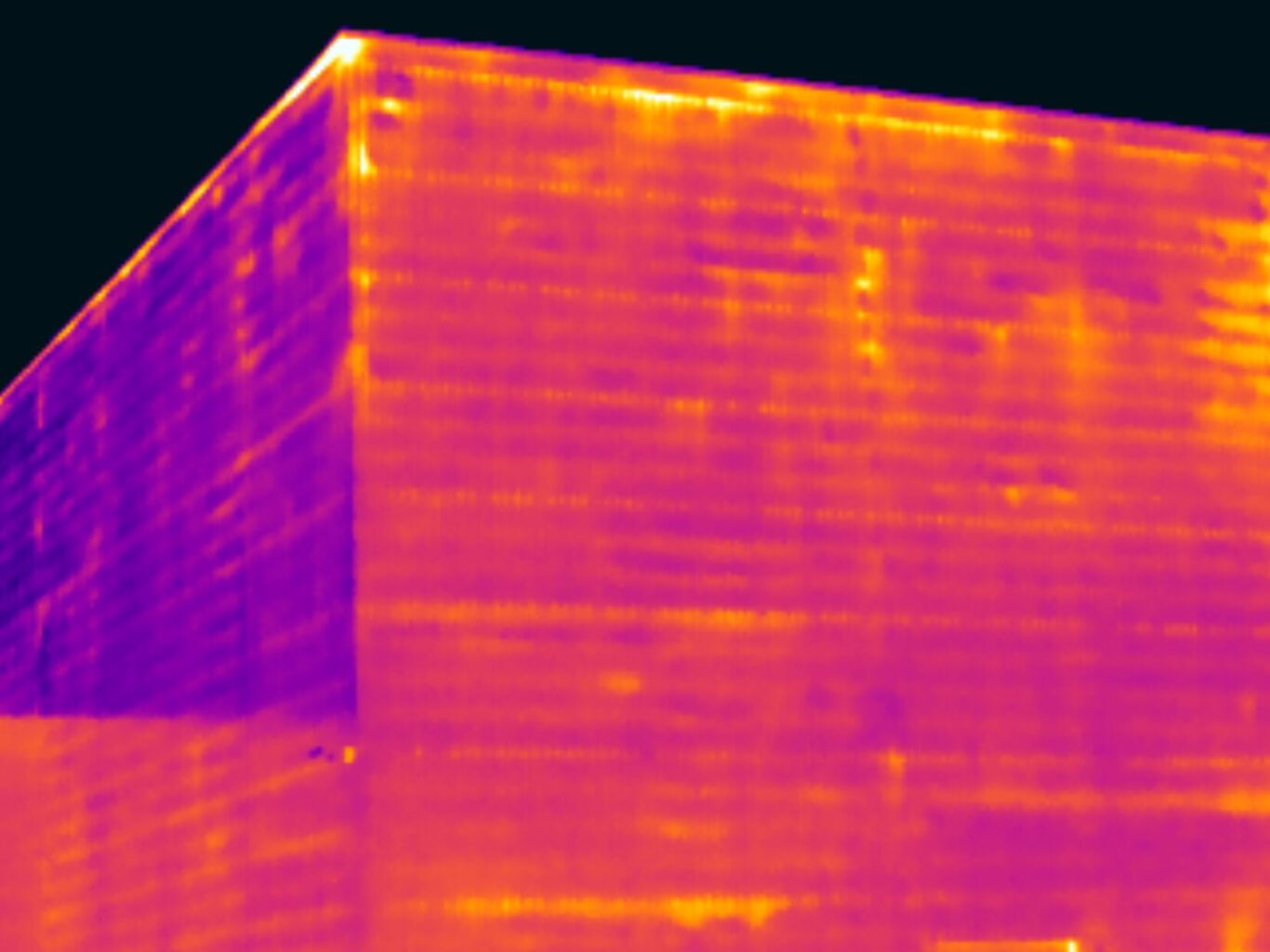
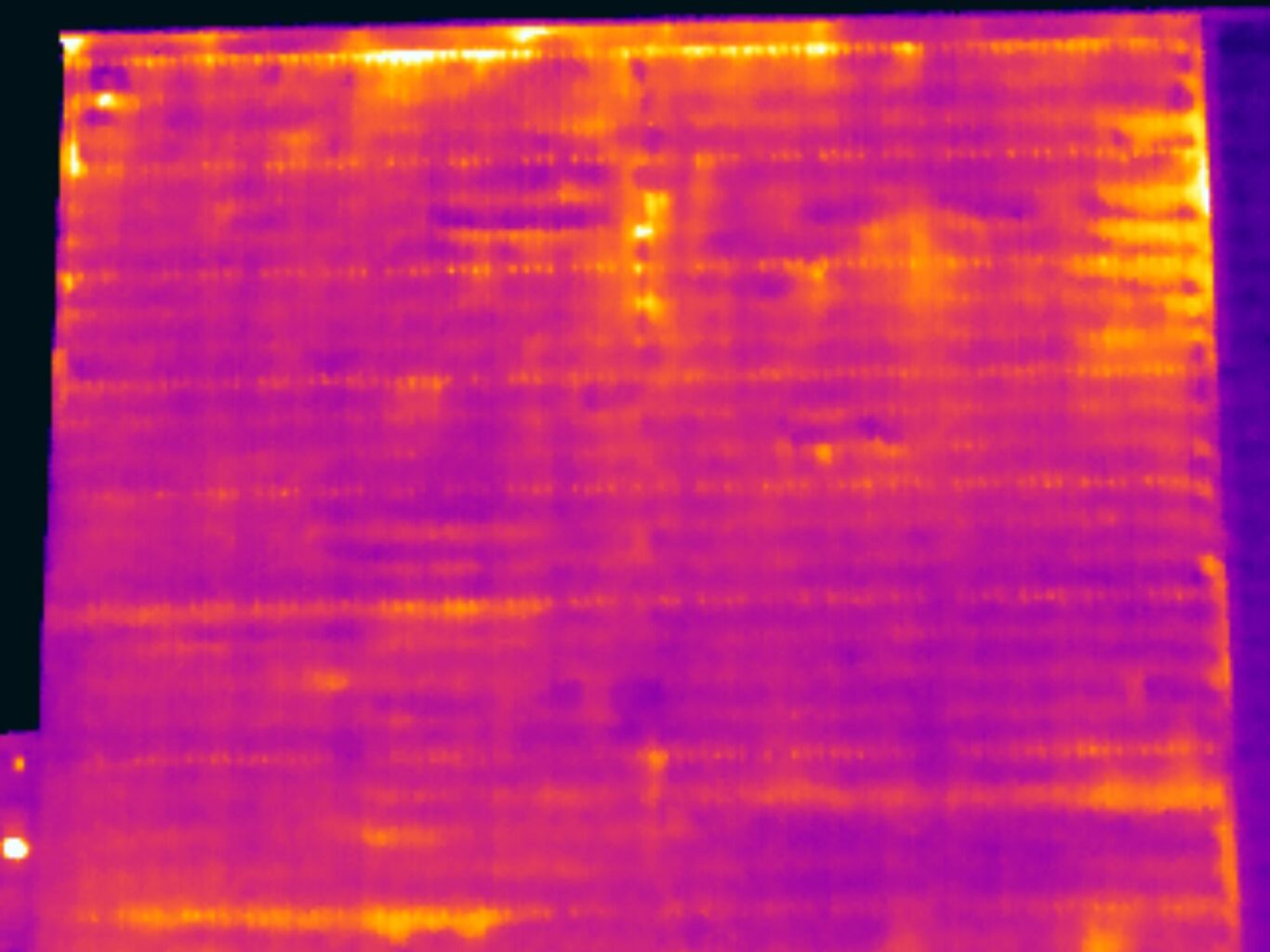
Thermal bridging through wall fabrication fixings
Understanding Thermal Bridging:
Thermal bridging occurs when a conductive material provides a pathway for heat to bypass the insulation, creating a direct route for heat to escape or enter a building. In commercial buildings, common thermal bridges include structural elements like steel or concrete connections, as well as poorly insulated junctions between walls and floors.
Effects on Heat Loss:
The repercussions of thermal bridging are far-reaching, impacting both the energy efficiency and environmental sustainability of commercial buildings. Heat loss through thermal bridges forces heating systems to work harder to maintain desired indoor temperatures, resulting in increased energy consumption and higher utility bills.
Financial Implications:
The financial toll of thermal bridging is significant, as increased energy consumption directly translates to higher operational costs for businesses. Commercial buildings with poor thermal performance face a double-edged sword – not only do they incur greater expenses for heating, cooling, and ventilation, but they also contribute more to carbon emissions, facing potential regulatory and reputational consequences.
In addition to operational costs, the long-term maintenance expenses of a building can skyrocket due to the wear and tear caused by constant temperature fluctuations resulting from thermal bridging. By addressing this issue during the design and construction phases, businesses can make an investment in sustainable and cost-effective infrastructure.
Thermal Imaging: A Precision Tool for Detection:
To combat the adverse effects of thermal bridging, the construction industry turns to advanced technologies, with thermal imaging taking center stage. This non-intrusive method allows professionals to identify thermal irregularities in buildings by capturing and analysing the infrared radiation emitted by surfaces.
Thermal imaging cameras detect temperature variations, revealing hidden thermal bridges that may not be apparent through traditional methods. This technology provides an invaluable visual representation of heat distribution across a building, aiding architects, engineers, and energy assessors in pinpointing areas susceptible to thermal bridging.
Mitigating Thermal Bridging:
Armed with insights from thermal imaging, construction professionals can implement targeted strategies to mitigate thermal bridging and enhance the energy efficiency of commercial buildings. This may involve incorporating high-performance insulation materials, optimising building envelope design, and using thermal breaks to interrupt the flow of heat through structural elements.
Additionally, a holistic approach to construction, considering factors like airtightness and ventilation, can further minimise the impact of thermal bridging. By integrating these measures into building projects, businesses can future-proof their structures against rising energy costs and environmental challenges.
Building Surveys using Thermography
We are experienced and certified level 2 category thermographers. We work boith from the air using specialist thermal drone technology as well as on the ground using traditional building thermal imaging techiques to inspect commericla and domestic properties.
Thermography is a non-destructive and non-invasive technology looking at the anomolies, faults and observations covering moisture, water ingress, insulation continuity, heat loss, air leakage, thermal bridging and insect infiltration.
In the pursuit of sustainable and energy-efficient commercial buildings, understanding and addressing thermal bridging is paramount. The financial and environmental consequences of overlooking this phenomenon can be substantial.
Through the lens of thermal imaging, the construction industry gains a powerful tool to identify and rectify thermal bridging issues, paving the way for a future where buildings are not only aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible and cost-effective. As the demand for energy-efficient structures continues to rise, embracing technologies like thermal imaging becomes not just a choice but a necessity for a resilient and sustainable built environment.
Expert Infrared Inspections for Accurate Thermal Assessments
Need professional thermographic analysis for your project? Our certified experts use the latest infrared technology to deliver precise results. Contact Drone Media Imaging today for expert thermal imaging services.











